Search Engine Optimization, also abbreviated as SEO, is a generalized technique that encompasses the art of improving readership and directing traffic to websites through search engines such as Google, Yahoo and Bing.
It is a subset of the larger syndicate of Search Engine Marketing (SEM) that incorporates both natural search results as well as paid advertorials. Hence, this technique specifically aims to generate as many algorithmic and ‘organic’ results as possible, in comparison to paid advertorials that pop up in a search result.
[vooplayer type=”video” id=”MTM1NTY0″ float=”right-25%” ]
The impetus
“Why is it important to engage in search engine optimization?”, you might ask. Let us visit some statistics. Google amasses 3.5 billion search queries every single day. That translates to approximately the same number of website visitor-ship per day, and each day lost translates into a loss of viewership.
Paid advertorials are displayed transparently on search engines– a tricky road to crawl down if you do not have large starting capital, as well as knowing the fact that consumers are able to discern between advertorials and organic results.
In the world of business, this is a crucial component in affecting website visibility.
As your website is more tailored towards the tenets of SEO, it will rank higher on international search engine indexes- inviting readership to reap itself as potential business clients.
This can be achieved by simple steps such as looking for specific keywords that will be picked up by search engines, as well as adding related content (images, GIFs) related to your industry that can be indexed.
History of SEO
The history of SEO dates back to 1997 when Danny Sullivan, Google’s search division advisor decided to popularize the term with the advent of search engines on the public domain.
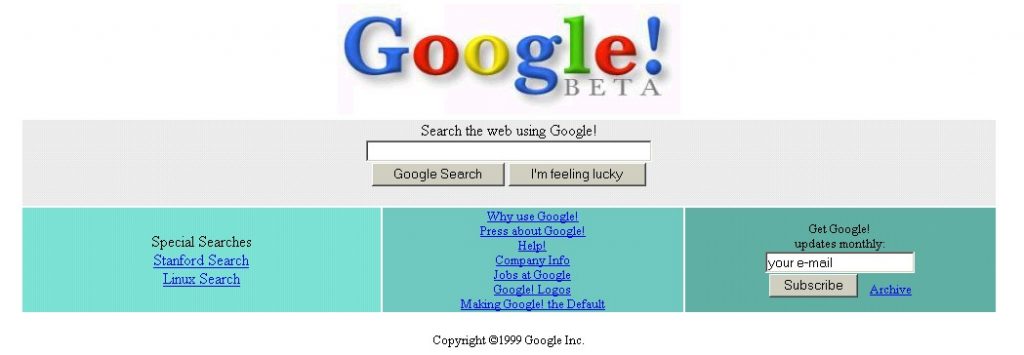 In its early years, search engine optimisation was practiced by website hosts (also known as webmasters) sending domains through web crawlers, robots that efficiently sifts through websites for indexing purposes.
In its early years, search engine optimisation was practiced by website hosts (also known as webmasters) sending domains through web crawlers, robots that efficiently sifts through websites for indexing purposes.
This was an immensely fruitful process to take advantage of, given the fact that website visibility could be easily tampered by the type of websites that the web crawlers index.
However, this had led to some unethical practices involving spam indexing- this differentiates ‘white hat’ ethical SEO indexing from ‘black hat’ unethical SEO indexing. For the purpose of this article, white hat indexing is recommended and we will explore that further on.
The basic rules and recommendations to make your website SEO-friendly comes in a series of steps.
- The websites should be made primarily for users and not merely search engines. It is easier to do the latter by creating a webpage that is merely keyword after keyword, flashing after another. However, this would defeat the purpose of amassing a dedicated clientele.
- Your website should have a formidable structure. Links directing the user to other pages should be clearly stated, as well as an organizational hierarchy.
- Your website must be informational and provide some sort of usefulness to the reader. It should have adequate data supplying your organization or business, and it must also be clear enough to be easily comprehensible.
- Your links should be short and reader-friendly.A link that has a catch and is easily remembered would surely perform better compared to a site with a convoluted domain name.
Search engine optimization still works on the foundational tenets of web crawlers, however, it has branched out into two subfields- on-page and off-page SEO.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO relays the methodology that the website undergoing search engine optimization should be changed or tampered with to reflect certain fixtures that will catapult the website into getting indexed higher by web crawlers. This can be achieved through identifying three defining tenets that will make or break on-page SEO– links, content, and page structure.
Links
As mentioned in the basic rules, the link should be short and reader-friendly, but it must also contain your business’ defining keyword.

For example, if your main imperative is to market a car wash, your domain should go along the lines
of ‘www.bosoncarwash.com’ instead of ‘boson’ or anything else that marks out of the said territory.
Also, the correct domain ending would also allow the web crawlers to categorize your website more efficiently. For example, if you are an organization, it is advisable to optimize your website by ending it with a ‘.org’, or if you are an educational institution, ‘.edu’.
Page structure
Now, we will tackle the art of page structure. Your keyword should be visible in your website’s title tag, as this sets the tone and command for the rest of the page.
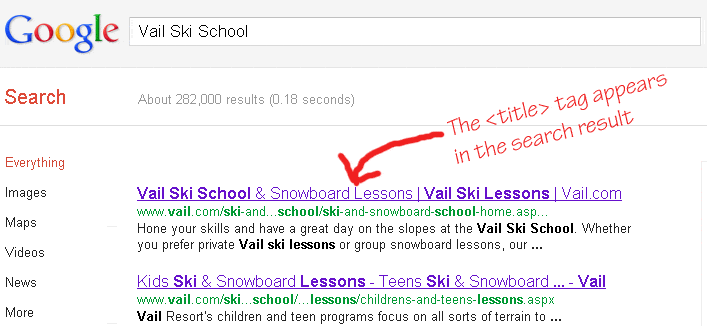
This can also be reflected in the form of a site header or banner, where the title should embody the keyword. A meta-description or a tagline with your desired keywords will also be useful
It will be reflected in the search indexes as a ‘description’ of your website and potentially making future clientele drawn to visit your website.
Website Content
Lastly, the content of your website is also very important as the web crawlers garner an algorithm of the defining keywords of your webpage and hence, search for it amongst your webpage to boost its credibility in the domain of the said keyword.
In any variation of your body text or article writing, do add your keyword(s) into the text about 2 to 3 times. Frequency will allow the web crawlers to generate a totality of the keyword that you wish to market. Pictorial sources will also boost the repertoire of your website, but be sure to add your keyword or an iteration of it in the description.
Moreover, adding a sitemap will aid web crawlers in indexing your website faster and much higher. The content should also strive to be new and be replenished daily, as the less dormant your website is, the greater the search indexing.
An advantage would also be optimizing your website to have a mobile-friendly interface, as Google’s search indexes also vary for websites that are only able to function in only one medium. Web pages with a versatile desktop to mobile formatting tend to also get higher indexes, as well as web pages that load fast.
Off-Page SEO
Off page search engine optimization, on the other hand, does not deal with the website that you intend to market. It deals with the way websites are cross-referenced by other websites or contain many cross-references from other websites, as well as marketing through appearances in vertical list searches (search engines that are specialized for certain industries, such as Yelp, and HungryGoWhere) and it can aid in link building as well. Or simply, the “share” button on social media that we are all familiar with can act as a link aggregator for off-page SEO building.
Link building is the most preferred way of off-page search engine optimization.
This includes adding links from other websites as ‘sources’ for your articles, or the other way round, with other websites citing your website as a source.
The most popular website utilizing this method of search engine optimization would be Wikipedia, as most of its material originate from other websites, and this pays back as many people cite Wikipedia.
To achieve this, you have to constantly target industry groups that are trying to advertise and optimise the same keywords that you intend to market. For example, you can be a contributor on a gardening site and cite your own gardening website as the source.
Other light forms of off-page SEO include adding your website as forum signatures, in which you can sign up for forums related to your business’ industry and leave your website as the signature.
Comment links could also help, as you take advantage of networking to leave comments about your website on other websites/blog pages relating to the same industry as your business.
However, on-page SEO has more credibility as it directly works with the search indexing of web crawlers. It may be harder to market through off-page SEO unless you already do have a marketing circle.
With this, I have covered the basic tenets of search engine optimization as well as the two main defining methods of SEO. Stay tuned for more information on SEO-related topics!